
3 Anatomy Surrounding the Eye OpticianWorks Online Optician Training Human anatomy and
The structures and functions of the eyes are complex. Each eye constantly adjusts the amount of light it lets in, focuses on objects near and far, and produces continuous images that are instantly transmitted to the brain. The orbit is the bony cavity that contains the eyeball, muscles, nerves, and blood vessels, as well as the structures that.
Human Eye Anatomy, parts and structure Online Biology Notes
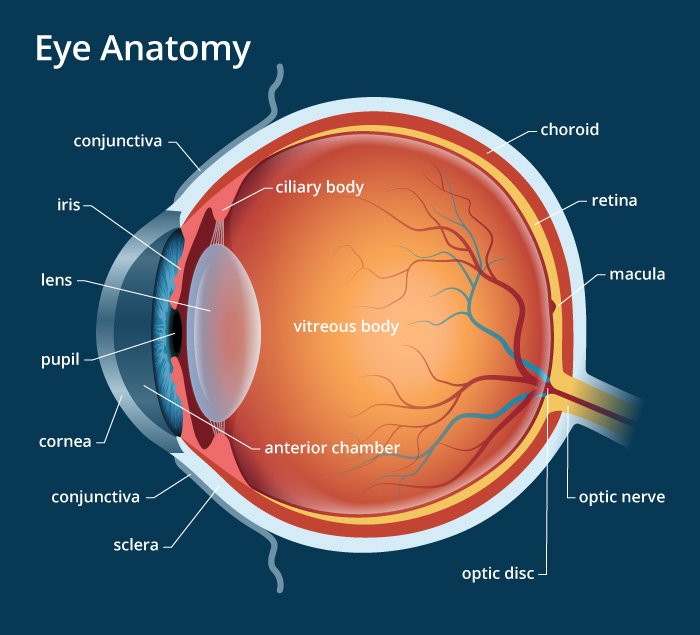
Muscles in the iris dilate (widen) or constrict (narrow) the pupil to control the amount of light reaching the back of the eye. Directly behind the pupil sits the lens. The lens focuses light toward the back of the eye. The lens changes shape to help the eye focus on objects up close.

Eye Anatomy
The main parts of the human eye are the cornea, iris, pupil, aqueous humor, lens, vitreous humor, retina, and optic nerve. Light enters the eye by passing through the transparent cornea and aqueous humor. The iris controls the size of the pupil, which is the opening that allows light to enter the lens. Light is focused by the lens and goes.
/GettyImages-695204442-b9320f82932c49bcac765167b95f4af6.jpg)
Structure and Function of the Human Eye
Light is focused primarily by the cornea - the clear front surface of the eye, which acts like a camera lens. The iris (colored part) of the eye functions like the diaphragm of a camera, controlling the amount of light reaching the retina by automatically adjusting the size of the pupil (aperture). The eye's crystalline lens is located.
Human Eye Labelled Diagram , Free Transparent Clipart ClipartKey
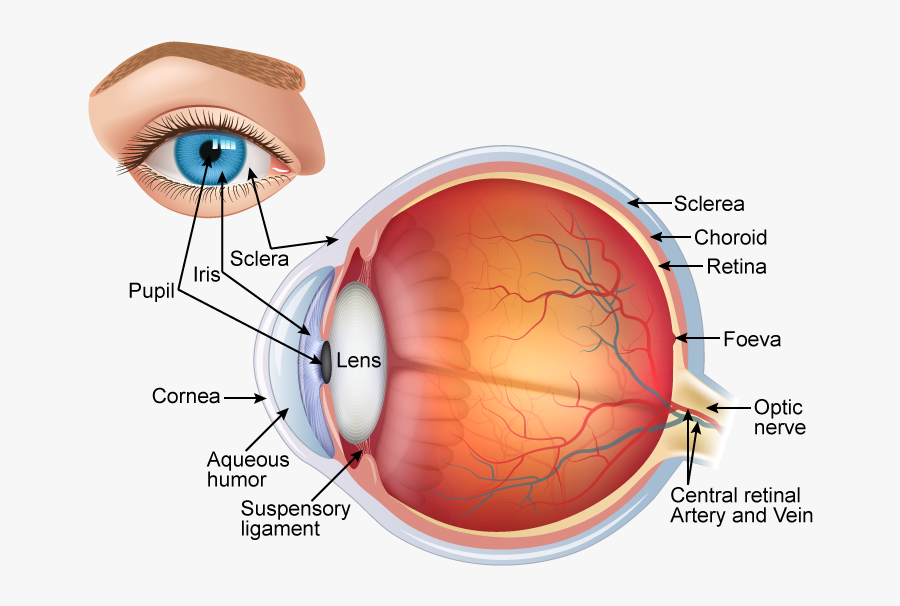
Labeled Diagram of Human Eye . The eyes of all mammals consist of a non-image-forming photosensitive ganglion within the retina which receives light, adjusts the dimensions of the pupil, regulates the availability of melatonin hormones, and also entertains the body clock.

Human eye Extraocular Muscles Britannica
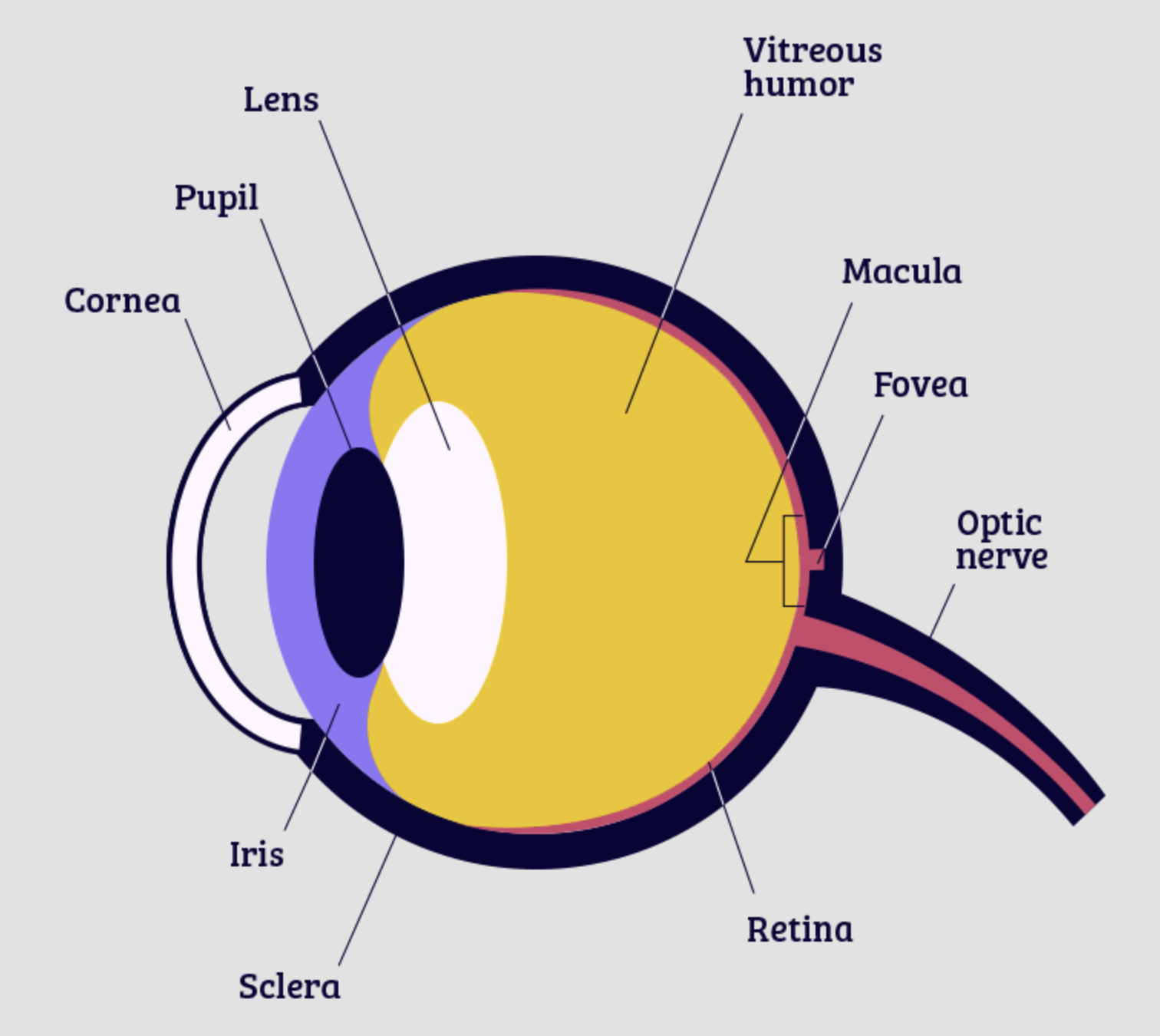
Cornea: The clear, dome-shaped tissue covering the front of the eye. Fovea: A tiny pit located in the macula of the retina that provides the clearest vision of all. Iris: The colored part of the eye that controls the amount of light that enters the eye by changing the size of the pupil. Lens: A crystalline structure located just behind the iris.

Human Eye Anatomy Parts of the Eye and Structure of the Human Eye
Diagram Of Eye The human eye is responsible for the most important function of the human body, the sense of sight. It consists of several distinct parts that work in coordination with each other. The most common eye diseases include myopia, hypermetropia, glaucoma and cataract.
HUMAN EYE (STRUCTURE, IMAGE FORMATION AND DIFFERENCE BETWEEN RODS AND CONES) « SimpleBiology
The iris is a flat, thin, ring-shaped structure sticking into the anterior chamber. This is the part that identifies a person's eye colour. The iris contains both circular muscles going around the pupil and radial muscles radiating toward the pupil. When the circular muscles contract, they make the pupil smaller.
About the Eye National Eye Institute
Labeled diagram of the eye Diagram showing the parts of the eye with labels So, how can you use them to your benefit? Take a look at the diagram of the eyeball above. Here you can see all of the main structures in this area.

File1413 Structure of the Eye.jpg Wikimedia Commons
Labelling the eye — Science Learning Hub Interactive Labelling the eye Interactive Add to collection Use this interactive to label different parts of the human eye. Drag and drop the text labels onto the boxes next to the diagram. Selecting or hovering over a box will highlight each area in the diagram. Cornea Lens Retina Optic nerve Pupil Schlera

Can We Grow New Eyes?
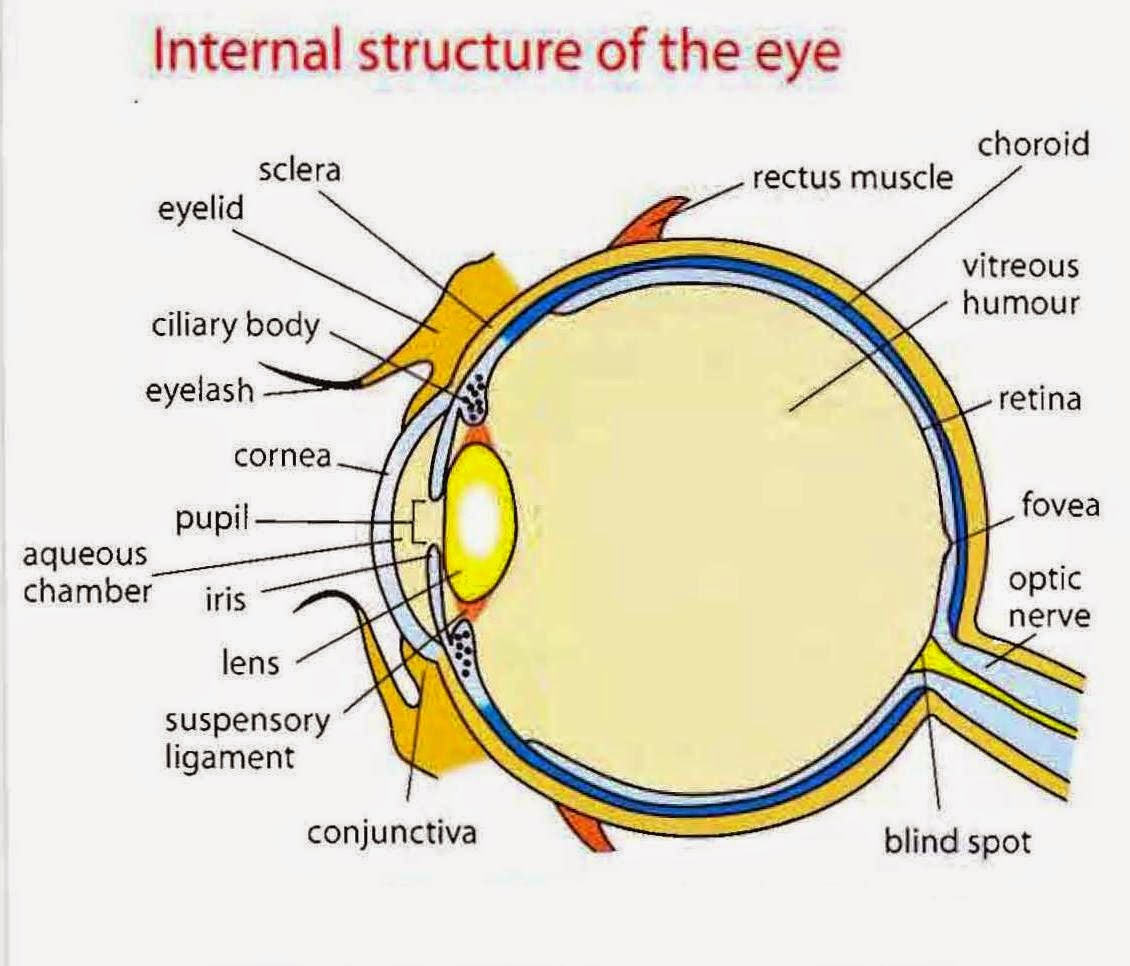
Eyelid anatomy Lacrimal gland Eye muscles Eyeball Outer layer Middle layer Inner layer Blood supply of the eye Nerves of the eye Sources + Show all Bones of the orbit The bony orbit is made out of seven bones, which include the maxilla, zygomatic bone, frontal bone, ethmoid bone, lacrimal bone, sphenoid bone and palatine bone.
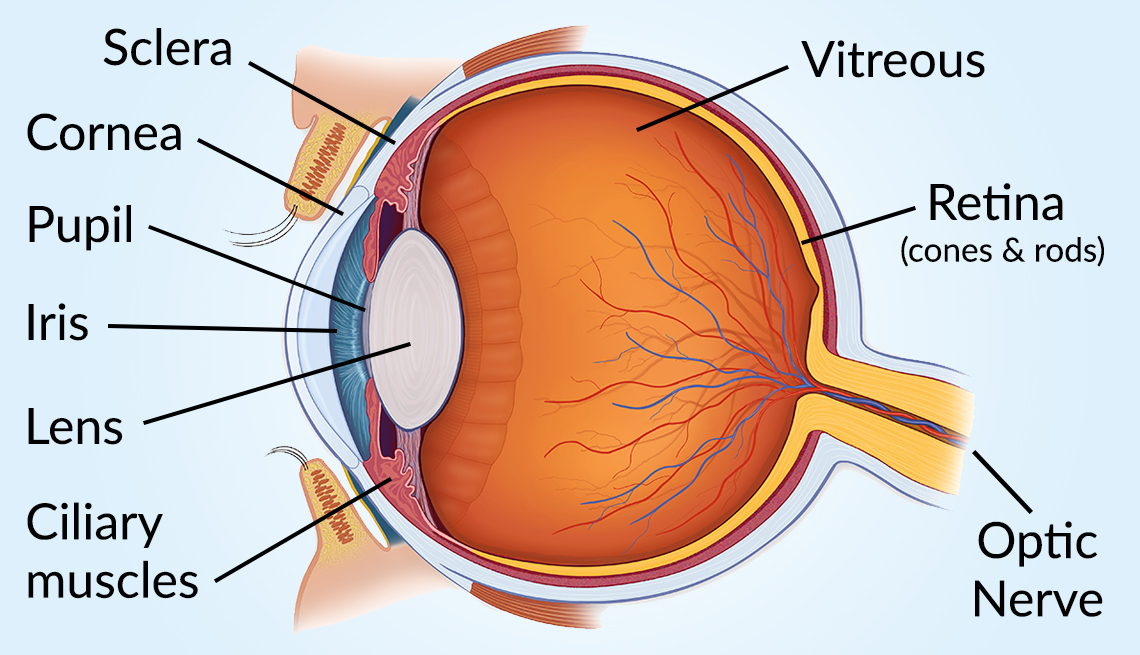
Vision and Eye Diagram How We See
Human Eye Diagram: Contrary to popular belief, the eyes are not perfectly spherical; instead, it is made up of two separate segments fused together. Explore: Facts About The Eye To understand more in detail about our eye and how our eye functions, we need to look into the structure of the human eye. Recommended Video: 1,221
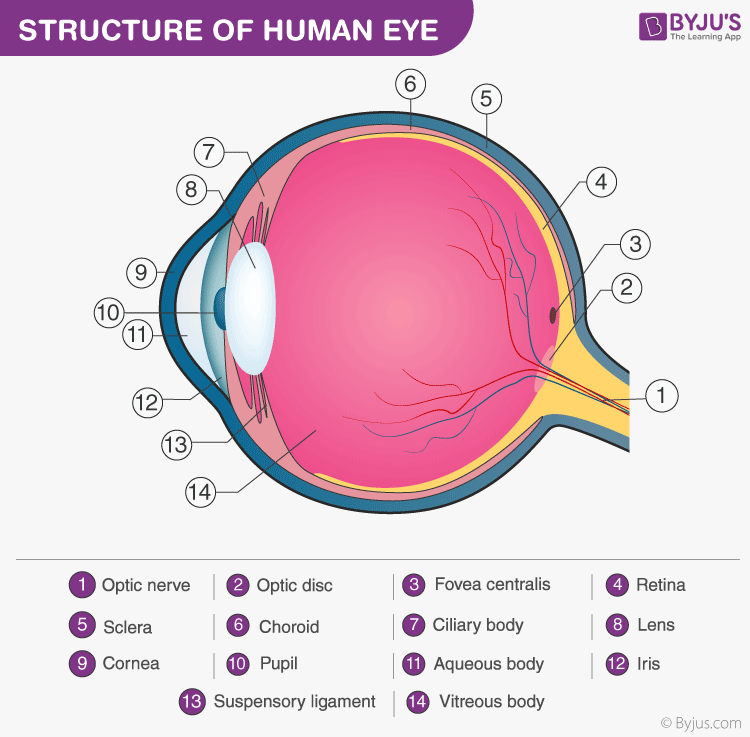
Human Eye Definition, Structure, Function, Parts, Diagram
Pads of fat and the surrounding bones of the skull protect them. The eye has several major components: the cornea, pupil, lens, iris, retina, and sclera. These work together to capture an image.

Diagram showing the different parts of the eye Parts of the eye, Eye health, Free homeschool
The eye is protected from mechanical injury by being enclosed in a socket, or orbit, which is made up of portions of several of the bones of the skull to form a four-sided pyramid, the apex of which points back into the head.

Brain Post How Big is Your Blind Spot? Human eye diagram, Eyeball structure
Diabetes Healthy ANATOMY and Eyes OF THE AND ITS FUNCTION Toolkit Parts of the Eye Vision is wonderful, but you could lose To understand it if you eye have problems, diabetes. it is helpful to know the different parts of the eye. Please refer to the back of this handout for descriptions of their functions. The main parts of the eye— Optic 3
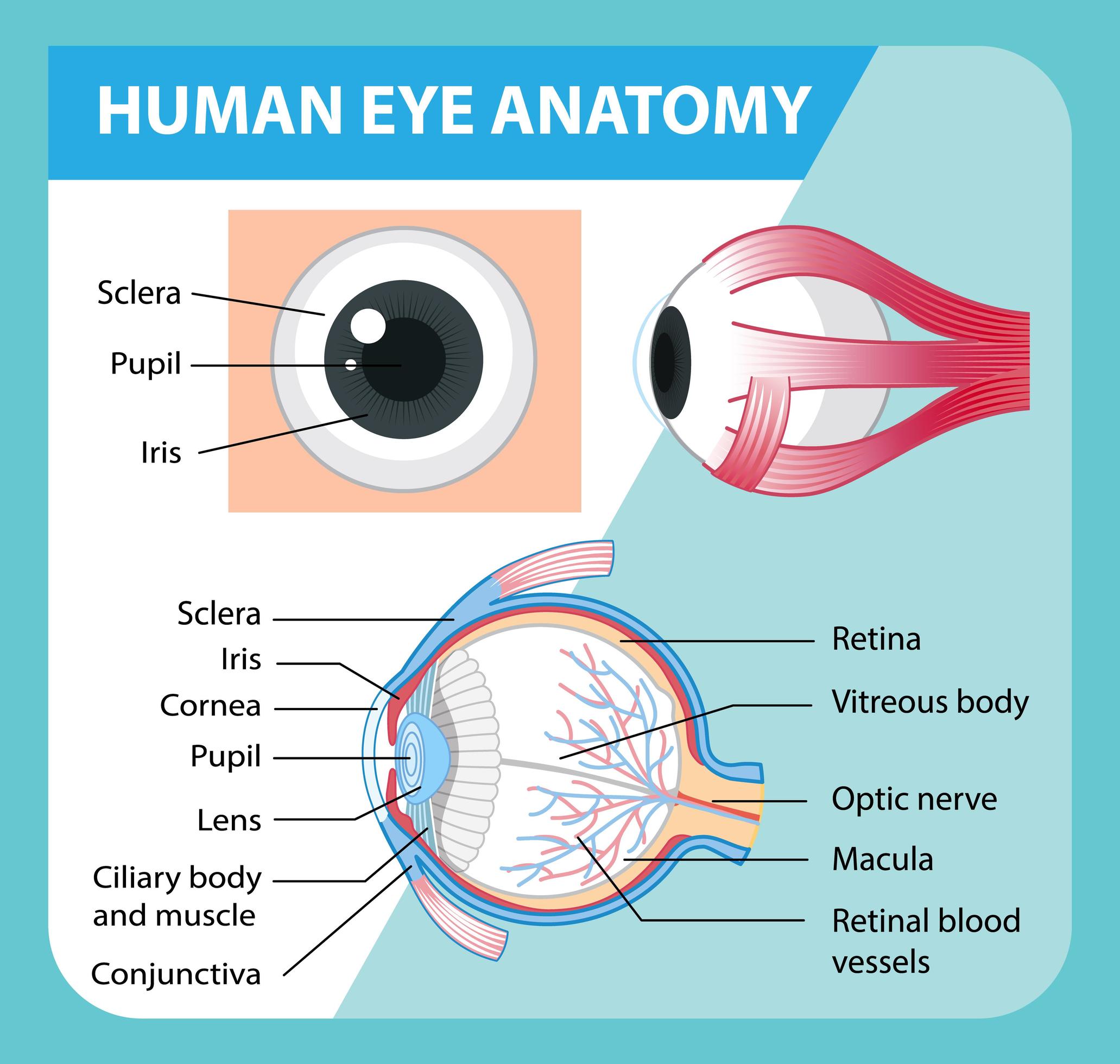
Diagram of human eye anatomy with label 1848847 Vector Art at Vecteezy
1. Conjunctiva The conjunctiva is the membrane covering the sclera (white portion of your eye). The conjunctiva also covers the interior of your eyelids. Conjunctivitis, often known as pink eye, occurs when this thin membrane becomes inflamed or swollen. Other eye disorders that affect the conjunctiva include: