How Are Light Microscopes And Electron Alike Shelly Lighting
The key difference between light and electron microscope is that a beam of electrons is employed for magnifying the image of an object while visible light is used in the light microscope to magnify images of spotted areas of materials or biological specimens.

What Are The Main Differences Between A Light Microscope And An Electron Microscope
In actuality there are two main types, namely the light microscope vs electron microscope. Most likely you are familiar with a light microscope. This version sits on a desk, uses light and a lens to magnify your objects, and is often found in science classes around the world.

Light microscope vs. Electron microscope
Light vs Electron Microscope: What's the Difference? (With Pictures) Last Updated on Jul 23 2023 When you need to see the smallest of subjects in great detail, you turn to the microscope. But there are multiple types of microscopes and they're each suited for different viewing purposes.
How Are Compound Light Microscopes And Electron Alike Shelly Lighting
Greg Foot explains the main differences between light and electron microscopes A replica of Robert Hooke's compound microscope We need microscopes to study most cells. Microscopes are.
Differences between Light Microscope and Electron Microscope
The main difference between them is that in an electron microscope, a beam of electrons is used for magnifying the image of an object while visible light is used in the light microscope to magnify images of tiny areas of materials or biological specimens.

Light vs Electron Microscopes YouTube
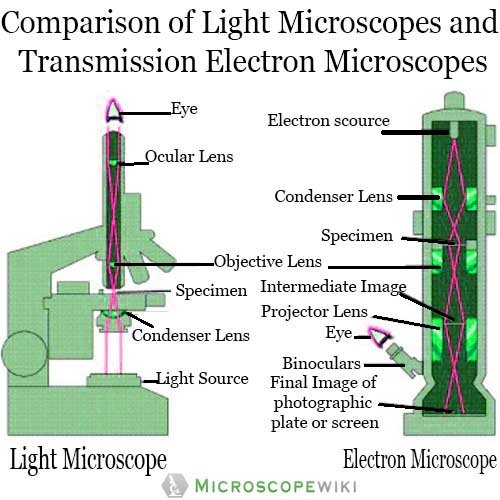
There are two fundamental types of microscopes; they are optical (light) microscopes which employ glass lenses and visible spectrum of light; and electron microscope which employ electromagnetic lenses and beam of electrons for image formation.

Difference between Light Microscope and Electron Microscope (Light Microscope vs Electron
Light microscopes are easy to operate, while electron microscopes show hidden features and have superior resolution. Budget, sample size, and detail level determine which equipment is best for a scientific inquiry. New imaging methods and hybrid systems may help us discover the invisible world as technology advances.

Microscopy GCSE Biology Science) Edexcel Revision Study Rocket
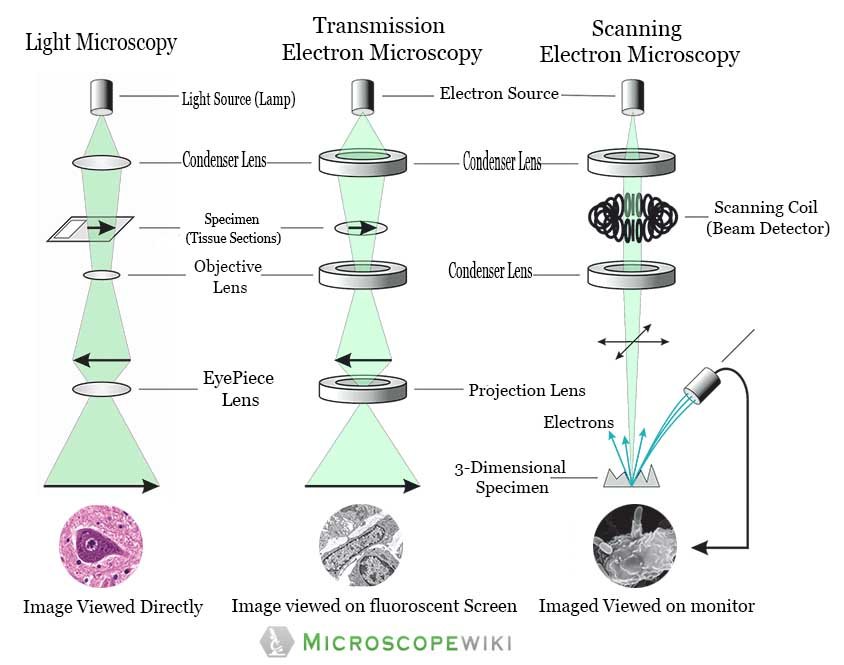
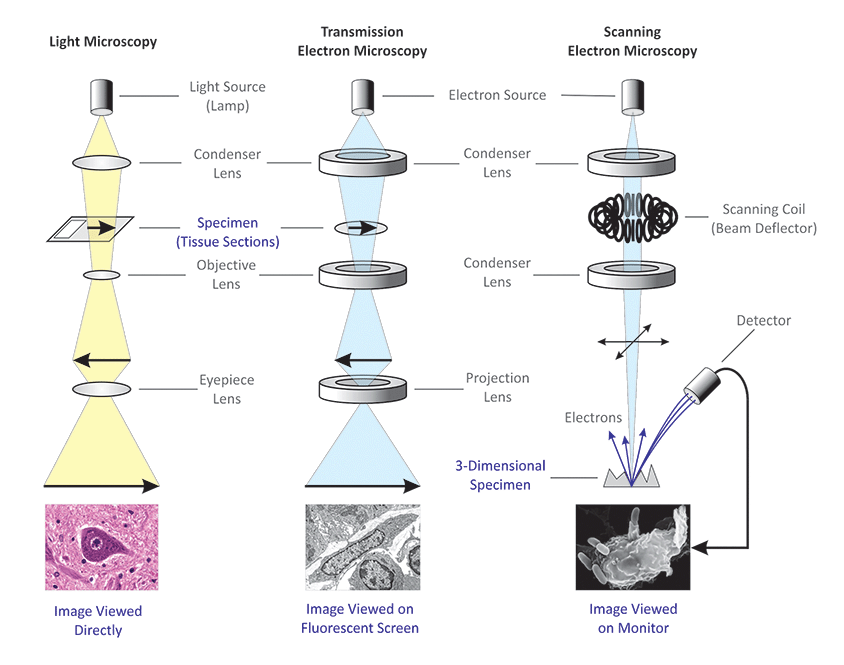
Microscopy Introduction to microscopes and how they work. Covers brightfield microscopy, fluorescence microscopy, and electron microscopy. Introduction If you meet some cell biologists and get them talking about what they enjoy most in their work, you may find it comes down to one thing: secretly, they're all microscope freaks.
Microscope
A light microscope utilizes a beam of light to observe tiny microorganisms like mitochondria, whereas an electron microscope, such as scanning electron microscope, uses a beam of electrons to enlarge a minuscule specimen. Let's have a brief overview of these microscopes through a comparison chart, and move towards details. Table of Contents

Light microscope vs. Electron microscope
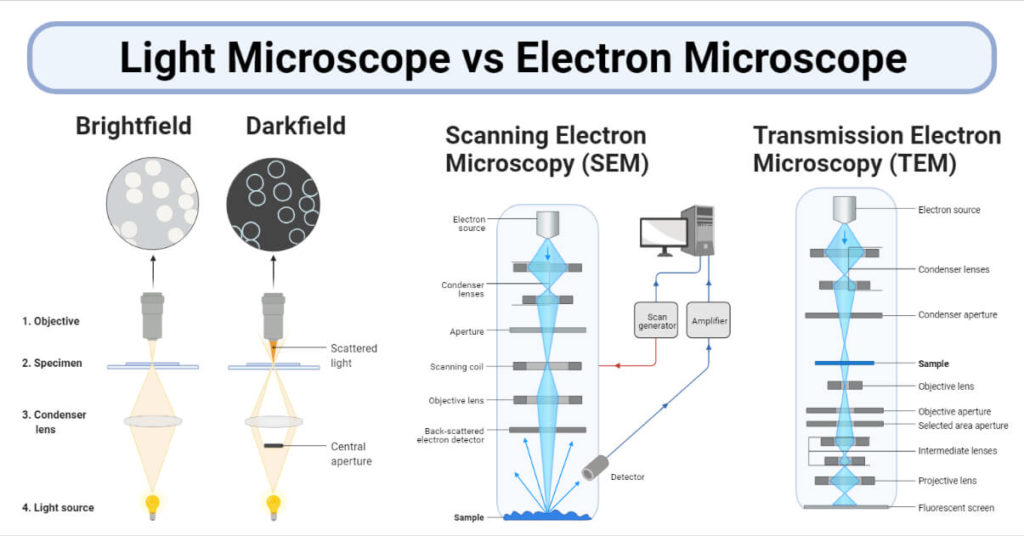
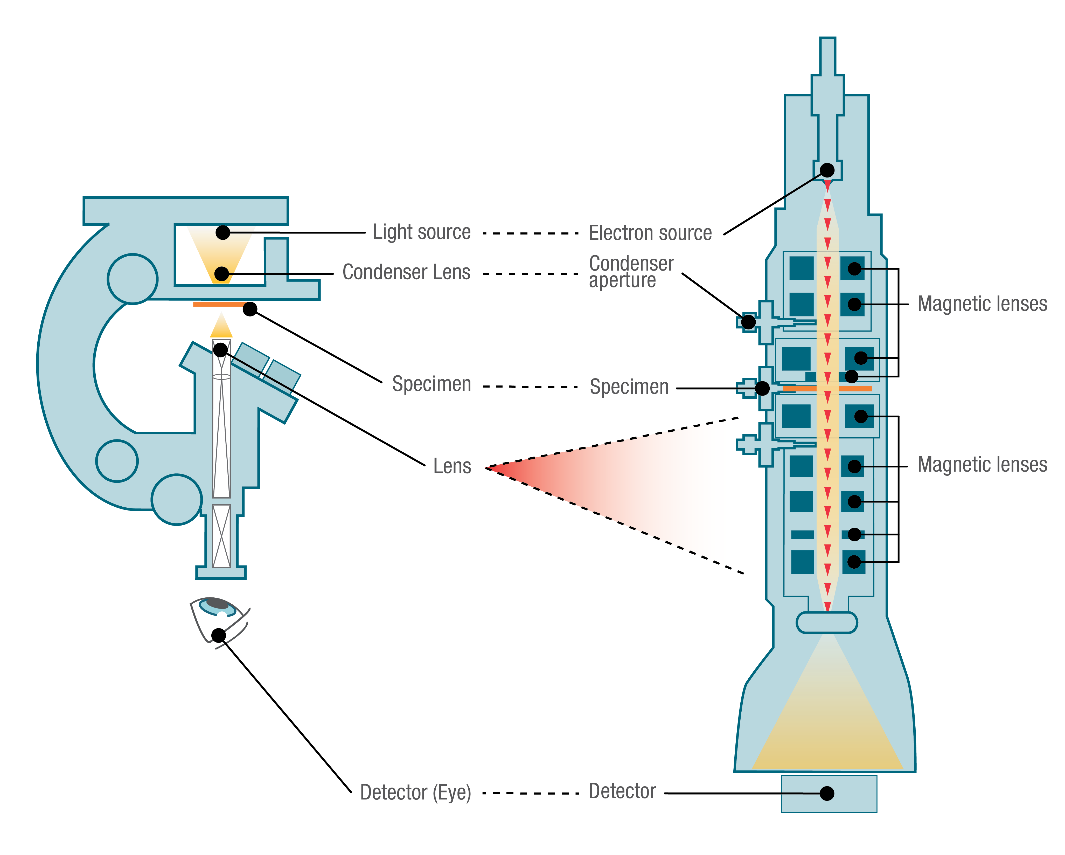
In a light, or optical, microscope, a light source is placed below the sample, which must be thin enough to allow some light to pass through. (If it isn't, the object will appear dark, and no details can be discerned.) The light is focused onto the sample with a condenser lens, resulting in a focused point of light on the specimen's surface.
Light vs Electron Microscope What's the Difference? (With Pictures) Optics Mag
Light Microscopes vs. Electron Microscopes. Most microscopes used in college biology laboratories are classified as light microscopes (see the figure, part (a) below) and may also be called compound microscopes since they use two lenses whose magnifications compound (multiply). Visible light passes through the specimen and is bent through the.

Light microscope vs. Electron microscope
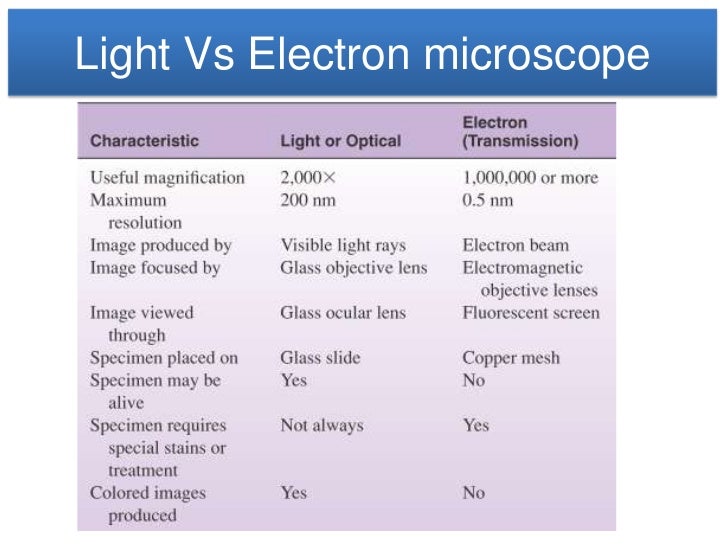
Differences: Size: Light microscopes are smaller and lighter, so are easier to move and set-up. Cost / Availability: Light microscopes are less expensive than electron microscopes. Radiation Type: Light microscopes use light (approx wavelength 400-700 nm), electron microscopes use beams of electrons (approx equivalent wavelength 1 nm).
Light Microscope vs Electron Microscope 36 Major Differences
Light Microscope vs. Electron Microscope Last Updated on February 16, 2022 By Excedr Microscopes are high-tech equipment that enable us to see the world at an entirely different level. What most people don't know is that the first compound microscope was created in 1590, by Dutch spectacle makers Hans and Zacharias Janssen.

😍 Compound light microscope vs electron microscope. The Comparison of a Light Microscope to an
One of the characteristic difference is that a light microscope uses a light source, whereas an electron microscope uses a beam of an electron. The light microscope shows low magnifying and resolving power of 1000X and 0.2µm, respectively. In contrast, an e - microscope shows high magnifying and resolving power of 10, 00,000X and 0.001µm.
Light Microscope vs Electron Microscope Life in Atomic Resolution
The main difference between light and electron microscopes is the radiation used to form an image; the 'light' and 'electron' in the names refer to the radiation being used. Using visible light as a radiation has several limitations, which the electron microscope lessens. However, light microscopes are much more practical in general use.

Difference between Light and Electron Microscope Microscope Crew
Light Microscope. Electron Microscope. Illuminating source is the Light. Illuminating source is the beam of electrons. Specimen preparation takes usually few minutes to hours. Specimen preparation takes usually takes few days. Live or Dead specimen may be seen. Only Dead or Dried specimens are seen. Condenser, Objective and eye piece lenses are.